数据结构实战
本文作者:李德强
第一节 二叉树
首先我们来简单的学习一下二叉树的存储结构:
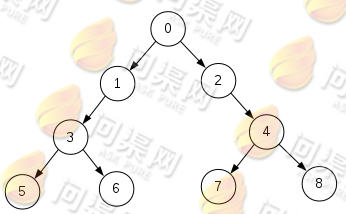
二叉树是普通树的一种特殊形式,二叉树的每一个数据节点都有一个节点称作父节点(或双亲节点)和两个子节点,称作左孩子和右孩子。当然,对于根节点来说,它的父节点必为空。而对于所有非根节点来说,父节点必然存在。对于最底层叶子节点来说,它们的左右孩子节点必为空。其它节点的左右孩子节点可以为空也可以非空。下面来看一下二叉树的数据结构:
//二叉树节点
typedef struct s_node
{
//数据指针
void *data;
//父节点
struct s_node *parent;
//左孩子节点
struct s_node *left_child;
//右孩子节点
struct s_node *right_child;
} s_node;
//二叉树数据结构
typedef struct s_tree
{
//根节点
s_node *root;
//访问函数指针
void (*visit_node)();
//释放内存函数指针
void (*free_node)();
} s_tree;
接下来实现二叉树的一些常用功能函数:
//初始化树
bool tree_init(s_tree *tree, void (*visit_node)(), void (*free_node)())
{
if (tree == null)
{
return false;
}
tree->root = null;
tree->visit_node = visit_node;
tree->free_node = free_node;
return true;
}
//销毁树
bool tree_destroy(s_tree *tree)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return false;
}
//清空树
tree_clear(tree, tree->root);
//根节点置空
tree->root = null;
return true;
}
//清空树
void tree_clear(s_tree *tree, s_node *node)
{
if (node == null)
{
return;
}
//递归清空左子树
tree_clear(tree, node->left_child);
//递归清空右子树
tree_clear(tree, node->right_child);
//如果数据项不为空
if (node->data != null)
{
//释放数据项内存
tree->free_node(node->data);
}
node->left_child = null;
node->right_child = null;
if (node == tree->root)
{
tree->root = null;
}
//释放当前节点内存
free(node);
}
//取得根节点
s_node* tree_root(s_tree *tree)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return null;
}
return tree->root;
}
//找到数据项在树中的节点
bool tree_find_node(s_node *node, s_node **node_f, void *data)
{
if (node == null)
{
return false;
}
if (node_f == null)
{
return false;
}
if (data == null)
{
return false;
}
//找到同地址数据项,返回当前节点
if (node->data == data)
{
*node_f = node;
return true;
}
//递归查找左子树
if (tree_find_node(node->left_child, node_f, data))
{
return true;
}
//递归查找右子树
if (tree_find_node(node->right_child, node_f, data))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
//找到数据项在树中的父节点
s_node* tree_parent(s_tree *tree, void *data)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return null;
}
if (data == null)
{
return null;
}
//找到数据项所在的节点
s_node *node_find = null;
tree_find_node(tree->root, &node_find, data);
if (node_find == null)
{
return null;
}
//返回父节点
return node_find->parent;
}
//找到数据项在树中的左孩子
s_node* tree_left_child(s_tree *tree, void *data)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return null;
}
if (data == null)
{
return null;
}
//找到数据项所在的节点
s_node *node_find = null;
tree_find_node(tree->root, &node_find, data);
if (node_find == null)
{
return null;
}
//返回左孩子节点
return node_find->left_child;
}
//找到数据项在树中的右孩子
s_node* tree_right_child(s_tree *tree, void *data)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return null;
}
if (data == null)
{
return null;
}
//找到数据项所在的节点
s_node *node_find = null;
tree_find_node(tree->root, &node_find, data);
if (node_find == null)
{
return null;
}
//返回右孩子节点
return node_find->right_child;
}
//找到数据项在树中的左兄弟
s_node* tree_left_brother(s_tree *tree, void *data)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return null;
}
if (data == null)
{
return null;
}
//找到数据项所在的节点
s_node *node_find = null;
tree_find_node(tree->root, &node_find, data);
if (node_find == null)
{
return null;
}
if (node_find->parent == null)
{
return null;
}
if (node_find == node_find->parent->left_child)
{
return null;
}
//返回左兄弟
return node_find->parent->left_child;
}
//找到数据项在树中的右兄弟
s_node* tree_right_brother(s_tree *tree, void *data)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return null;
}
if (data == null)
{
return null;
}
//找到数据项所在的节点
s_node *node_find = null;
tree_find_node(tree->root, &node_find, data);
if (node_find == null)
{
return null;
}
if (node_find->parent == null)
{
return null;
}
if (node_find == node_find->parent->right_child)
{
return null;
}
//返回右兄弟
return node_find->parent->right_child;
}
//将node_ins插入node的左或右节点,原节点做为node_ins的右节点
bool tree_insert(s_tree *tree, s_node *node, int leftright, s_node *node_ins)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return false;
}
if (node_ins == null)
{
return false;
}
//如果是一棵空树
if (tree->root == null)
{
//将节点做为树的根节点
tree->root = node_ins;
node_ins->parent = null;
return true;
}
//被插入节点的右子树必须为空
if (node_ins->right_child != null)
{
return false;
}
//如果插入目标节点的左节点
if (leftright == 0)
{
//插入左节点
s_node *p_temp = node->left_child;
node->left_child = node_ins;
node_ins->parent = node;
//将原左子树挂接到新节点的右子树上
node_ins->right_child = p_temp;
if (p_temp != null)
{
p_temp->parent = node_ins;
}
}
//如果插入目标节点的右节点
else if (leftright == 1)
{
//插入右节点
s_node *p_temp = node->right_child;
node->right_child = node_ins;
node_ins->parent = node;
//将原右子树挂接到新节点的右子树上
node_ins->right_child = p_temp;
if (p_temp != null)
{
p_temp->parent = node_ins;
}
}
return true;
}
//删除节点
void tree_delete_node(s_tree *tree, s_node *node)
{
if (node == null)
{
return;
}
//递归删除左子树
tree_delete_node(tree, node->left_child);
//递归删除右子树
tree_delete_node(tree, node->right_child);
if (node->data != null)
{
tree->free_node(node->data);
}
//删除左节点
node->left_child = null;
//删除右节点
node->right_child = null;
//如果是根节点则清空树
if (node == tree->root)
{
tree->root = null;
}
free(node);
}
//删除树的节点
bool tree_delete(s_tree *tree, s_node *node, int leftright)
{
if (tree == null)
{
return false;
}
if (node == null)
{
return false;
}
//删除左子树
if (leftright == 0)
{
tree_delete_node(tree, node->left_child);
node->left_child = null;
}
//删除右子树
else if (leftright == 1)
{
tree_delete_node(tree, node->right_child);
node->right_child = null;
}
//如果是根节点则清空树
if (node == tree->root)
{
tree->root = null;
}
return true;
}
对于树这种数据结构来说,很多函数通常都使用递归来实现的,这与树的数据结构一致。因为树的一个叶子节点可以看做是另外一棵树,而这棵树的每一个节点同样也都可以看作是另外的树。
最后来编写一个main函数对二叉树的数据结构做一些测试:
//删除整数函数
void free_int(int *i)
{
if (i != null)
{
free(i);
}
}
//访问整数函数
void visit_int(int *i)
{
if (i != null)
{
printf("%d", *i);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **args)
{
int *t0 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t1 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t2 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
*t0 = 0;
*t1 = 1;
*t2 = 2;
//初始化树
s_tree tree;
tree_init(&tree, &visit_int, &free_int);
s_node *n0 = (s_node *) malloc(sizeof(s_node));
s_node *n1 = (s_node *) malloc(sizeof(s_node));
s_node *n2 = (s_node *) malloc(sizeof(s_node));
n0->parent = null;
n0->left_child = null;
n0->right_child = null;
n0->data = t0;
n1->parent = null;
n1->left_child = null;
n1->right_child = null;
n1->data = t1;
n2->parent = null;
n2->left_child = null;
n2->right_child = null;
n2->data = t2;
//插入根节点
s_node *node = tree.root;
tree_insert(&tree, node, 0, n0);
//插入根节点的左孩子
node = tree.root;
tree_insert(&tree, node, 0, n1);
//插入根节点的右孩子
node = tree.root;
tree_insert(&tree, node, 1, n2);
//得到根节点
s_node *p = tree_root(&tree);
visit_int(p->data);
printf("\n");
//得到父节点
p = tree_parent(&tree, t1);
visit_int(p->data);
printf("\n");
//得到父节点
p = tree_parent(&tree, t2);
visit_int(p->data);
printf("\n");
//得到左孩子
p = tree_left_child(&tree, t0);
visit_int(p->data);
printf("\n");
//得到右孩子
p = tree_right_child(&tree, t0);
visit_int(p->data);
printf("\n");
//得到左兄弟
p = tree_left_brother(&tree, t2);
visit_int(p->data);
printf("\n");
//得到右兄弟
p = tree_right_brother(&tree, t1);
visit_int(p->data);
printf("\n");
//删除根节点的左孩子
tree_delete(&tree, tree.root, 0);
p = tree_left_child(&tree, t0);
if (p == null)
{
printf("Left child of the root node is null.\n");
}
//删除根节点的右孩子
tree_delete(&tree, tree.root, 1);
p = tree_right_child(&tree, t1);
if (p == null)
{
printf("Right child of the root node is null.\n");
}
//销毁树
tree_destroy(&tree);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
0 0 0 1 2 1 2 Left child of the root node is null. Right child of the root node is null.
本例代码:
code path chapter.05/e.g.5.1/ https https://github.com/magicworldos/datastructure.git git git@github.com:magicworldos/datastructure.git subverion https://github.com/magicworldos/datastructure
Copyright © 2015-2023 问渠网 辽ICP备15013245号