数据结构实战
本文作者:李德强
第一节 线性表的顺序表示
本节我们来学习线性表的顺序表示。首先定义一些必要数据类型:
typedef int bool; #define true (1) #define false (0) #define null ((void *)0)
这些数据类型在后续的章节中不再重复说明。
顺序线性表与数组类似,程序可以通过向操作系统申请一段连续的内存空间并在这段连续的空间内进行数据操作。其内存结构图如下:
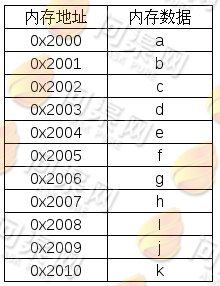
现在我们来实现一个顺序线性表,首先看一下顺序线性表的数据结构:
//表节点
typedef struct
{
void *data;
} s_node;
//表数据结构
typedef struct
{
//元素大小
int ele_size;
//目前元素个数
int length;
//表总大小
int size;
//内存空间的首地址
void *header;
//用于释放节点数据的回调函数
void (*free_data)();
//用于访问节点数据内容的回调函数
void (*visit_data)(void *data);
} s_list;
我们为了能让这个顺序表能够存放任意类型的数据,所以在s_node结构中使用了void *data这样的通用指针来指向一个任意类型的数据结构。
接下来实现一些顺序表的函数:
//构建一个顺序线性表
bool init_list(s_list *list, int ele_size, void (*free_data)(), void (*visit_data)())
{
if (list == null)
{
return false;
}
//申请数据所在的内存空间
list->header = malloc(sizeof(s_node) * INIT_SIZE);
if (list->header == null)
{
return false;
}
list->ele_size = ele_size;
list->size = INIT_SIZE;
list->length = 0;
list->free_data = free_data;
list->visit_data = visit_data;
return true;
}
//销毁表
bool destroy_list(s_list *list)
{
if (list == null)
{
return false;
}
if (list->header == null)
{
return true;
}
clear_list(list);
free(list->header);
return true;
}
//清空表中所有元素
bool clear_list(s_list *list)
{
if (list == null || list->header == null)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; ++i)
{
//计算元素位置
s_node *node = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + (i * sizeof(s_node)));
list->free_data(node->data);
}
list->length = 0;
return true;
}
//取得表中现有元素个数
int list_length(s_list *list)
{
if (list == null)
{
return 0;
}
return list->length;
}
//取得在第i个位置元素的数据内容
bool get_element(s_list *list, int i, void *e)
{
if (list == null || list->header == null || e == null)
{
return false;
}
//计算元素位置
s_node *node = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + (i * sizeof(s_node)));
//复制元素数据到e中
memcpy(e, node->data, list->ele_size);
return true;
}
//在第i个位置前插入一个新元素
bool list_insert(s_list *list, int i, void *e)
{
if (list == null || list->header == null || e == null)
{
return false;
}
if (i != 0 && i >= list->length)
{
return false;
}
//超过当前最大容量,请申原容量的2倍
if (list->length + 1 > list->size)
{
//申请新空间
void *p = realloc(list->header, list->size * sizeof(s_node) * 2);
if (p == null)
{
return false;
}
list->header = p;
list->size *= 2;
}
//创建新节点
s_node *p_ele = (s_node *) malloc(sizeof(s_node));
if (p_ele == null)
{
return false;
}
//数据
p_ele->data = e;
//从尾到i依次向后移动一个单元
for (int j = list->length; j > i; --j)
{
s_node *node_pre = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + ((j - 1) * sizeof(s_node)));
s_node *node_curr = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + (j * sizeof(s_node)));
memcpy(node_curr, node_pre, sizeof(s_node));
}
//插入新元素
s_node *node = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + (i * sizeof(s_node)));
memcpy(node, p_ele, sizeof(s_node));
//长度加1
list->length++;
return true;
}
//删除第i个元素
bool list_delete(s_list *list, int i)
{
if (list == null || list->header == null)
{
return false;
}
if (i >= list->length)
{
return false;
}
//计算元素位置
s_node *node = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + (i * sizeof(s_node)));
list->free_data(node->data);
//从i+1依次向前移动一个单元
for (int j = i; j < list->length - 1; ++j)
{
s_node *node_curr = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + (j * sizeof(s_node)));
s_node *node_next = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + ((j + 1) * sizeof(s_node)));
memcpy(node_curr, node_next, sizeof(s_node));
}
list->length--;
return true;
}
//对每个元素执行visit操作
bool list_visit(s_list *list)
{
if (list == null || list->header == null)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; ++i)
{
//计算元素位置
s_node *node = (s_node *) ((char *) list->header + (i * sizeof(s_node)));
list->visit_data(node->data);
}
return true;
}
最后写一个main函数来测试顺序表分别存放int型数据和结构体数据:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "list.h"
void free_int(void *data)
{
free(data);
}
void print_int(void *data)
{
printf("%d\n", *((int *) data));
}
typedef struct
{
int no;
int age;
char *name;
} student;
void print_stu(void *data)
{
student *stu = (student *) data;
printf("no:%d age:%d name:%s\n", stu->no, stu->age, stu->name);
}
void free_stu(void *data)
{
student *stu = (student *) data;
free(stu->name);
free(stu);
}
int main(int argc, char **args)
{
//用于存放int型数据的list
s_list list_int;
//释放内存函数与访问函数均是int型
init_list(&list_int, sizeof(int), free_int, print_int);
//插入数据
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
int *e = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
*e = i;
list_insert(&list_int, 0, e);
}
//显示list中所有数据内容
list_visit(&list_int);
//销毁list
destroy_list(&list_int);
printf("\n");
//用于存放student型数据的list
s_list list_stu;
//释放内存函数与访问函数均是student型
init_list(&list_stu, sizeof(student), free_stu, print_stu);
//插入数据
student *stu1 = (student *) malloc(sizeof(student));
stu1->no = 15100101;
stu1->age = 23;
stu1->name = (char *) malloc(20);
memcpy(stu1->name, "lidq", 20);
list_insert(&list_stu, 0, stu1);
//插入数据
student *stu2 = (student *) malloc(sizeof(student));
stu2->no = 15100102;
stu2->age = 21;
stu2->name = (char *) malloc(20);
memcpy(stu2->name, "zhaoy", 20);
list_insert(&list_stu, 0, stu2);
//插入数据
student *stu3 = (student *) malloc(sizeof(student));
stu3->no = 15100103;
stu3->age = 22;
stu3->name = (char *) malloc(20);
memcpy(stu3->name, "liuzh", 20);
list_insert(&list_stu, 0, stu3);
//显示list中所有内容
list_visit(&list_stu);
//销毁list
destroy_list(&list_stu);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4 3 2 1 0 no:15100103 age:22 name:liuzh no:15100102 age:21 name:zhaoy no:15100101 age:23 name:lidq
本例代码:
code path chapter.01/e.g.1.1/ https https://github.com/magicworldos/datastructure.git git git@github.com:magicworldos/datastructure.git subverion https://github.com/magicworldos/datastructure
#1楼
好朋友
于 2017年09月13日11:08:06 发表
不错不错
#2楼
李德强
于 2017年09月13日13:51:13 发表
感谢您对问渠网的支持!
#3楼
umee
于 2017年10月23日23:11:27 发表
好文章啊,跟着学习了
Copyright © 2015-2023 问渠网 辽ICP备15013245号