数据结构实战
本文作者:李德强
第二节 线性表的链式表示
我们先来看一下线性表的链式表示(以下称为链表)图:

也就是说链表中每一个节点中都存在一个指针,这个指针用于指向下一个节点,也就是指向下一个节点的内存地址。
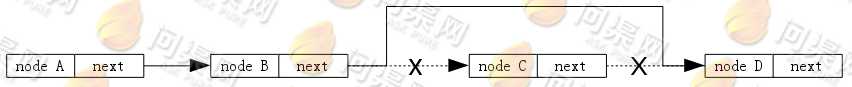
下面再来看一下在链表的第i个节点前插入一个新节点:

删除第i个节点:
首先定义链表的数据结构:
//表节点
typedef struct s_node
{
void *data;
struct s_node *next;
} s_node;
//表数据结构
typedef struct
{
//元素大小
int ele_size;
//链表大小
int length;
//头节点
s_node *header;
//用于释放节点数据的回调函数
void (*free_data)();
//用于访问节点数据内容的回调函数
void (*visit_data)(void *data);
} s_list;
接下来实现一些顺序表的函数:
//构建一个顺序线性表
bool init_list(s_list *list, int ele_size, void (*free_data)(), void (*visit_data)())
{
if (list == null)
{
return false;
}
list->ele_size = ele_size;
list->length = 0;
list->free_data = free_data;
list->visit_data = visit_data;
list->header = null;
return true;
}
//销毁表
bool destroy_list(s_list *list)
{
if (list == null)
{
return false;
}
if (list->header == null)
{
return true;
}
clear_list(list);
return true;
}
//清空表中所有元素
bool clear_list(s_list *list)
{
if (list == null)
{
return false;
}
//从头节点开始释放
s_node *p = list->header;
while (p != null)
{
//释放内存
list->free_data(p->data);
s_node *t = p;
p = p->next;
free(t);
}
list->header = null;
list->length = 0;
return true;
}
//取得表中现有元素个数
int list_length(s_list *list)
{
if (list == null)
{
return 0;
}
return list->length;
}
//取得在第i个位置元素的数据内容
bool get_element(s_list *list, int i, void *e)
{
if (list == null || list->header == null || e == null)
{
return false;
}
s_node *p = list->header;
int j = 0;
while (p != null)
{
//找到第i个元素
if (j == i)
{
//复制元素数据到e中
memcpy(e, p->data, list->ele_size);
return true;
}
p = p->next;
j++;
}
return false;
}
//在第i个位置前插入一个新元素
bool list_insert(s_list *list, int i, void *e)
{
if (list == null || e == null)
{
return false;
}
if (i != 0 && i > list->length)
{
return false;
}
//申请新节点内存
s_node *p_new = (s_node *) malloc(sizeof(s_node));
p_new->data = e;
p_new->next = null;
//如果头节点为空
if (i == 0)
{
//设置头节点为插入元素
p_new->next = list->header;
list->header = p_new;
//长度加1
list->length++;
return true;
}
else
{
//在i-1与i之间位置插入
s_node *p = list->header;
int j = 0;
while (p != null)
{
//找到第i-1个元素
if (j == i - 1)
{
//插入新节点
p_new->next = p->next;
p->next = p_new;
//长度加1
list->length++;
return true;
}
p = p->next;
j++;
}
}
return false;
}
//删除第i个元素
bool list_delete(s_list *list, int i)
{
if (list == null || list->header == null)
{
return false;
}
if (i >= list->length)
{
return false;
}
//如果是头节点
if (i == 0)
{
s_node *p_del = list->header;
//删除头节点
list->header = list->header->next;
//释放内存
list->free_data(p_del->data);
free(p_del);
//长度减1
list->length--;
return true;
}
else
{
s_node *p = list->header;
int j = 0;
while (p != null)
{
//找到第i-1个元素
if (j == i - 1)
{
//删除第i个元素
s_node *p_del = p->next;
p->next = p_del->next;
//释放内存
list->free_data(p_del->data);
free(p_del);
//长度减1
list->length--;
return true;
}
p = p->next;
j++;
}
}
return false;
}
//对每个元素执行visit操作
bool list_visit(s_list *list)
{
if (list == null || list->header == null)
{
return false;
}
//顺序访问每一个元素
s_node *p = list->header;
while (p != null)
{
list->visit_data(p->data);
p = p->next;
}
return true;
}
最后写一个main函数来测试顺序表分别存放int型数据和结构体数据:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "list.h"
void free_int(void *data)
{
free(data);
}
void print_int(void *data)
{
printf("%d\n", *((int *) data));
}
typedef struct
{
int no;
int age;
char *name;
} student;
void print_stu(void *data)
{
student *stu = (student *) data;
printf("no:%d age:%d name:%s\n", stu->no, stu->age, stu->name);
}
void free_stu(void *data)
{
student *stu = (student *) data;
free(stu->name);
free(stu);
}
int main(int argc, char **args)
{
//用于存放int型数据的list
s_list list_int;
//释放内存函数与访问函数均是int型
init_list(&list_int, sizeof(int), free_int, print_int);
//插入数据
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
int *e = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
*e = i;
list_insert(&list_int, 0, e);
}
//显示list中所有数据内容
list_visit(&list_int);
//销毁list
destroy_list(&list_int);
printf("\n");
//用于存放student型数据的list
s_list list_stu;
//释放内存函数与访问函数均是student型
init_list(&list_stu, sizeof(student), free_stu, print_stu);
//插入数据
student *stu1 = (student *) malloc(sizeof(student));
stu1->no = 15100101;
stu1->age = 23;
stu1->name = (char *) malloc(20);
memcpy(stu1->name, "lidq", 20);
list_insert(&list_stu, 0, stu1);
//插入数据
student *stu2 = (student *) malloc(sizeof(student));
stu2->no = 15100102;
stu2->age = 21;
stu2->name = (char *) malloc(20);
memcpy(stu2->name, "zhaoy", 20);
list_insert(&list_stu, 1, stu2);
//插入数据
student *stu3 = (student *) malloc(sizeof(student));
stu3->no = 15100103;
stu3->age = 22;
stu3->name = (char *) malloc(20);
memcpy(stu3->name, "liuzh", 20);
list_insert(&list_stu, 2, stu3);
//显示list中所有内容
list_visit(&list_stu);
//销毁list
destroy_list(&list_stu);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4 3 2 1 0 no:15100101 age:23 name:lidq no:15100102 age:21 name:zhaoy no:15100103 age:22 name:liuzh
本例代码:
code path chapter.01/e.g.1.2/ https https://github.com/magicworldos/datastructure.git git git@github.com:magicworldos/datastructure.git subverion https://github.com/magicworldos/datastructure
Copyright © 2015-2023 问渠网 辽ICP备15013245号