数据结构实战
本文作者:李德强
第五节 深度优先搜索
图的顶点访问可以使用深度优先和广度优先两种搜索方法。深度优先即先访问一个顶点,接着访问这个顶点所能连通的其它顶点,而在多个连通的顶点中优先访问它们的连通节点。例如下图:
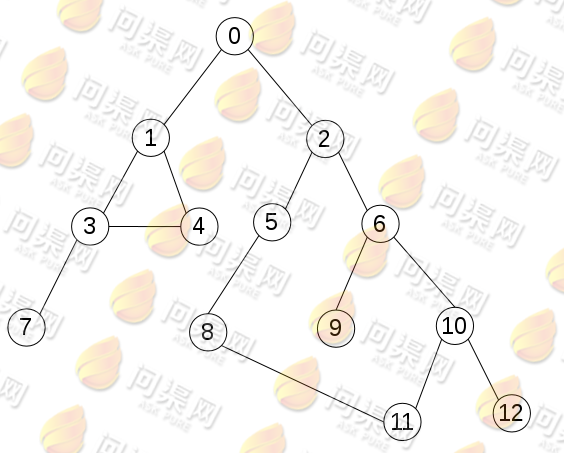
这个无向连通图如果从节点0开始,使用深度优先搜索结果为:
0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 7 -> 2 -> 5 -> 8 -> 11 -> 6 -> 9 -> 10 -> 12
深度优先的实现算法如下:
//深度优先搜索
bool graph_depth_first_search(s_graph *graph)
{
if (graph == null)
{
return false;
}
//设置顶点已访问标志
bool visited[graph->size];
for (int i = 0; i < graph->size; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
//访问所有的顶点
for (int i = 0; i < graph->size; i++)
{
//深度优先访问顶点
graph_dfs(graph, i, visited);
}
return true;
}
//深度优先访问顶点递归算法
void graph_dfs(s_graph *graph, int v_ind, bool *visited)
{
//如果此顶点已被访问,则直接返回
if (visited[v_ind])
{
return;
}
//设置此顶点为已访问
visited[v_ind] = true;
//调用访问回调函数访问此节点
graph->visit_vertex(graph->vertex[v_ind]);
//取得下一条边
s_arccell *ac = graph->vertex[v_ind].arccel_first;
//循环所有关联i的边
while (ac != null)
{
//深度优先访问
graph_dfs(graph, ac->i_index, visited);
//如果还有下一条j相关的边
s_arccell *ac_p = graph->vertex[ac->j_index].arccel_first;
while (ac_p != null)
{
//深度优先访问
graph_dfs(graph, ac_p->j_index, visited);
ac_p = ac_p->next_j;
}
//下一条i边
ac = ac->next_i;
}
}
main函数中构建图的顶点和边:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "graph.h"
void visit_int(int *i)
{
if (i != null)
{
printf("%d ", *i);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **args)
{
//邻接表
s_graph graph;
graph_init(&graph, 13, &visit_int, &visit_int);
//顶点数据项
int *t0 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t1 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t2 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t3 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t4 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t5 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t6 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t7 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t8 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t9 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t10 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t11 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
int *t12 = (int *) malloc(sizeof(int));
//顶点数据
*t0 = 0;
*t1 = 1;
*t2 = 2;
*t3 = 3;
*t4 = 4;
*t5 = 5;
*t6 = 6;
*t7 = 7;
*t8 = 8;
*t9 = 9;
*t10 = 10;
*t11 = 11;
*t12 = 12;
//设置顶点数据
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 0, t0);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 1, t1);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 2, t2);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 3, t3);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 4, t4);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 5, t5);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 6, t6);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 7, t7);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 8, t8);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 9, t9);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 10, t10);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 11, t11);
graph_set_vertex(&graph, 12, t12);
//插入边数据
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 0, 1, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 0, 2, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 1, 3, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 1, 4, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 2, 5, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 2, 6, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 3, 4, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 3, 7, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 5, 8, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 6, 9, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 6, 10, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 8, 11, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 10, 11, 0, null);
graph_insert_arccell(&graph, 10, 12, 0, null);
//显示顶点和边的关系
graph_visit(&graph);
//深度优先遍历图
graph_depth_first_search(&graph);
//销毁邻接表
graph_destroy(&graph);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
0 1 3 4 7 2 5 8 11 6 9 10 12
本例代码:
code path chapter.06/e.g.6.5/ https https://github.com/magicworldos/datastructure.git git git@github.com:magicworldos/datastructure.git subverion https://github.com/magicworldos/datastructure
Copyright © 2015-2023 问渠网 辽ICP备15013245号