跟我一起写操作系统
本文作者:李德强
第二节 输入函数
输入函数与输出函数有点不同,因为每个程序想要接受键盘的按键它们必须独占键盘设备。所以我们需要对每个想要接受按键的程序设置一个共享的按键信号量。注意,这个按键信号量是由内核程序创建并初始化的,这样才可以被普通进程所共享(因为所有的进程都共享使用低处内存)。内核创建一个全局按键信号量,并在安装键盘中断时将其初始化,信号量的值为1,也就是说在同一时刻只能有一个进程来使用这个资源:
//全局按键信号量
s_sem sem_key;
/*
* install_kb : 安装键盘中断
* return : void
*/
void install_kb()
{
//初始化全局按键信号量
sem_key.value = 1;
sem_key.list_block = NULL;
//打开IRQ1的键盘中断
outb_p(inb_p(0x21) & 0xfd, 0x21);
//清除键盘状态可以接受新按键
outb_p(0x7f, 0x61);
}
为0x81号信号量中断服务增加一个功能,让普通程序可以通过type取得不同类型的全局信号量,type为0代表是全局按键信号量:
//获取全局信号量
if (params[0] == 2)
{
int type = (int) params[1];
//按键信号量
if (type == 0)
{
s_sem **sem = (s_sem **) params[2];
sem = addr_parse(cr3, sem);
*sem = &sem_key;
}
}
为0x82号stdio中断服务加入接收按键的功能。当一个进程想要接受按键,则将这个进程挂起。等到键盘设备被按下时,为其设置按键的值并唤醒此进程:
if (params[0] == 0x10)
{
char *ch = (char *) params[1];
ch = addr_parse(cr3, ch);
ch_for_get = ch;
pcb_wait_key(pcb_cur);
}
在键盘中断服务中为请求接收按键的进程设置按键的值并唤醒此进程:
if (ch_for_get != NULL)
{
//得到按键
char ch = keys[key_ind - 1][kb_key_shift];
//为请求程序设置按键
*ch_for_get = ch;
//清空数据区
ch_for_get = NULL;
pcb_wakeup_key();
}
最后为普通shell程序来实现getchar函数从键盘接收一个按键:
char getchar()
{
char ch = 0;
//取得全局按键信号量
s_sem *sem = get_global_sem(0);
while (ch == 0)
{
sem_wait(sem);
int params[2];
params[0] = 0x10;
params[1] = (int)&ch;
__asm__ volatile ("int $0x82" :: "a"(params));
sem_post(sem);
}
return ch;
}
getchar()函数是其它输入函数的基础,我们将要实现的gets()函数和scanf()函数都是在getchar()函数的基础上实现的。首先来实现gets()函数,不断的从键盘中接收按键直到按键为回车符\n是停止:
void gets(char *str)
{
char ch, *p = str;
while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n')
{
*p = ch;
p++;
putchar(ch);
}
*p = '\0';
putchar('\n');
}
再实现一个函数get_int()用来接收一个整数:
int get_int()
{
char str[0x800];
char ch, *p = str;
char sign = 0;
do
{
ch = getchar();
if (ch == 0x8)
{
if (p > str)
{
p--;
backspace();
}
}
else if (sign == 0 && (ch == '+' || ch == '-'))
{
sign = ch;
putchar(ch);
}
else if (ch == '\n')
{
putchar(ch);
break;
}
else
{
*p = ch;
p++;
putchar(ch);
}
}
while (1);
*p = '\0';
p = str;
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; p[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
num = (int) p[i] - 48;
}
else
{
num *= 10;
num += (int) p[i] - 48;
}
}
if (sign == '-')
{
return -num;
}
return num;
}
最后是scanf()函数按格式接收输入:
void scanf(char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list args;
va_init(args, fmt);
while (*fmt != '\0')
{
if (*fmt == '%')
{
if ('c' == *(fmt + 1))
{
char *p = (char *) va_arg(args, u32);
*p = getchar();
putchar(*p);
fmt += 2;
}
else if ('s' == *(fmt + 1))
{
char *str = (char *) va_arg(args, u32);
gets(str);
fmt += 2;
}
else if ('d' == *(fmt + 1))
{
int *p = (int *) va_arg(args, u32);
*p = get_int();
fmt += 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
else
{
fmt++;
}
}
}
编写一个接收按键的程序example_stdio:
#include <kernel/string.h>
#include <shell/stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **args)
{
printf("Enter '\\n' to the end of the function 'getchar()'.\n");
char ch = 0;
do
{
ch = getchar();
putchar(ch);
}
while (ch != '\n');
printf("Enter \"exit\" to the end of the function 'gets()'.\n");
char str[0x200];
do
{
gets(str);
printf("%s\n", str);
}
while (str_compare("exit", str) != 0);
int i;
do
{
printf("Enter 0 for i to the end of the function 'scanf()'.\n");
printf("i = ");
scanf("%d", &i);
printf("ch = ");
scanf("%c", &ch);
printf("\n");
printf("str = ");
scanf("%s", str);
printf("i = %d\tch = %c\tstr = %s\n", i, ch, str);
}
while (i != 0);
printf("End of stdio example.\n");
return 0;
}
编译运行并查看结果:
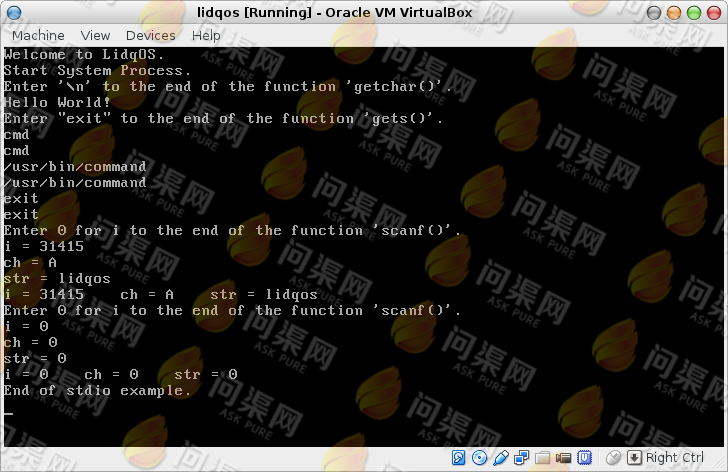
源代码的下载地址为:
https https://github.com/magicworldos/lidqos.git git git@github.com:magicworldos/lidqos.git subverion https://github.com/magicworldos/lidqos branch v0.25
Copyright © 2015-2023 问渠网 辽ICP备15013245号